OS Background Knowledge
All backgroud information needed for learning OS. Will be updated countineously.
OS as a Resource Manager
- File-System Management
- Create, deleting files and directories
- Supporting primitives for manipulating files and directories
- Mapping files onto mass storage
- Backing up files on stable(nonvalatile storage media)
- Mass-Storage Management
- Mounting and unmounting storage devices
- Free-space management
- Storage allocation
- Disk scheduling
- Partitioning
- Protection
- I/O System Management - via I/O subsystem
- A memory-management component with - buffering, caching, and spooling
- Make general uniform device-friver interface
- Cache management
- info is kept in some storage system. Check cache before need a particular piece of info
- Cache manage in a multiprogram system becomes tricky and even more in a multiprocessor environment
- Cache size and cache replacement policy
Evolution of OS
- Serial Processing
- Simple Batch Systems
- Multi-programmed Batch Sysems
- Time-Sharing Systems
Difference
| Batch Multi-prgramming | Time Sharing | |
|---|---|---|
| Principle Objective | Max processor use | Min response time |
| Source of intructions to operate system | Job control language JCL instructions provided with the job | Commands entered at the terminal |
Dual Mode Operation
- Kernal Model : Supervisor mode, system mode, privieged mode
- User Mode
A mode bit kernel 0 or user 1 is used to indicate the current mode.
Kernel Data Structure
- Array
- Each lement can be accessed directly
- List: Sequence of data value
- Singly linked list
- Doubly linked list
- Circular linked list: last point to the first
- Stacks
- Queues
- Tree / Binary Trees
- Hash functions
- Bitmaps: available table for resources
Linux Kernal Data Structure
- Linked-list data structure details are in the include file <linux/list.h>
- A queue in linus is know as kfifo, with implementation in kfifo.c file of kernel directory
- Implementation of the balanced binary search tree implementation using red-black trees can be found in the include file <linux/rbtree.h>
Virtualization
- Emulation - simulates computer hardware in software
- Virtualization - an OS that is natively compiled for a particular CPU architecture runs within another OS also native to that CPU
Distributed System
Network
Communication protocal
TCP/IP is the most common
Distance
- Local Area Network (LAN): room
- Wide Area Network (WAN): building
- Metropolitan-Area Network (MAN): city
- Personal-Area Network (PAN): BlueToothand 802.11 or other wireless
Communication Media
- Copper wires
- Fiber links
- Wireless trans between satellites
- Microware dishes
- Radio
- Infra-red
- ….
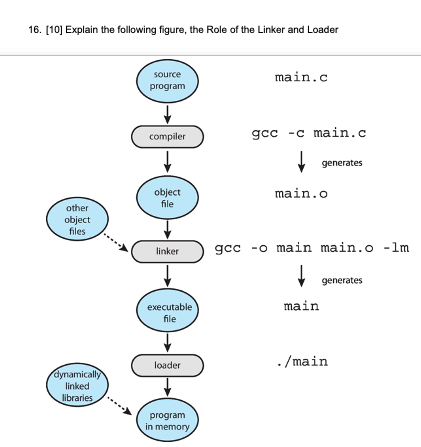
Loader and linker
- Relocatable object file - source code in complied into object files by the compiler and is designed to be loaded into any physical memory localtion
- Linker combines the object files into a single binary executable file
- also links the library object modules nedded by the program
- Loader brings the executable file into memory to run the program
- Relocation assign final addresses to program parts and adjusts code and data in program to match those address
- Modern negeral-purpose systems dont link library into executables
- but, hynamically linked libraries are loaded as needed, shared by all that use the same version of that same library
Computer System Architechture
- Most use single general-purpose processor
- some use special-purpose
- Multiprocessor System
- Parallel or tightly coupled systems
- offer
- increased throughput
- economy of scale
- increased reliability
- Two Type
- Asymmetric Multiprocessing (ASMP) - each processor is assigned a special task
- Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP) - each processor performs all tasks
| Asymmetric | Symmetric |
|---|---|
| All processor not equally | All equal |
| One master processor carries out the taskes of OS | Carried out by all processor |
| Processor cannot direct communicate with other processor (only via master) | All can communicate by a shared memory |
| Processes are categorized as master-slave | A ready queue is used for taking up processes |
| Cheaper | Relatively costly |
| Easier to design | Complex |
Dual Core Design
- A processor have two cores
- Each core has its own level 1 cache, but shared level 2 cache
Clustered Systems
- like multiprocessor systems, but multiples systems are working together in this case
- combine cheap multiple processing unit to provide high performance and efficient systems
- High-acailability service - continue even if one or more systems in the cluster fail
- Each node can monitor one or more of other nodes, in case of failure
- Users and clients see only a brief interruption of service
- Stotage shared by storage-area network SAN
- Types:
- Asymmetric clustering - one machine in hot-standby, other run application. If server fails, hot-standby becomes active server
- Symmetric clustering - multi nodes run app and monitor each other
- Use:
- High-performance computing HPC
- Fault tolerant mass data storage
- Graceful degradation
- OS design considerations and issues
- Load balancing
- Fair share of resources
- Communication overhead
Hadoop and Big Data
- High availability distributed object oriented platform - an open source sfwr framework for storing data and running app on clusters of commodity hardware
- In Java and run on Linux
- Provide massive storage for data, enormous processing power an handle huge # of concurrent tasks
- Not an OS, but frameware developed on top of Linux, giving it a distribured OS capability
- Its app can be written in many language
- Use it for big data
Computer Environment
- Traditional Computing
- Mobile Computing
- Client - Server Computing
- Compute-server systems
- File-server system (most web server)
- Peer to Peer P2P Computing
- Every node is a server and client
- Cloud Computing
- Public Cloud
- Private
- Hybrid
- SaaS
- PaaS
- IaaS
- Real-time Embedded Systems
Operating System Structure
- Monolithic Strcture - Tightly coupled system - shared memory
- All function of nernal placed in single, static binary file that run in single address space
- Run as a single program
- Original UNIX
- Typical use glibc standard C lib to communicate with kernel
- Linux has similar kernel but has a modular design that allows kernel to be modified during run time
- Layered Approach - lossly couples system - distributed memory
- brouen into number of layers
- Layer 0 (botton layer) is hardware, Highest layer N is the user interface
- Mth layer consists of data structures and function that can be invoked by higher layers
- Advantage
- Simplicity
- Debugging
- Each layer Hides existance of data struc, operations, and HW from higher level
- Can be used in computer network (like TCP/IP) and web app
- Microkernels

- Noneseential component are removed from the kernel
- Advantage
- easier extension
- easily ported from one hardware to other
- more security and reliability
- Drawbacks
- Copying of messages and switching between processir
- Modules
- UseLoadable Kernel Modules LKMs - best current method for OS design
- Kernel provide core services
- Futher service and be linked dynmically while kernel running
- Linking services does not require the recompilation of kernel
- Hybrid System
- Different structure combine
OS Background Knowledge