Strategy Pattern
Strategy Pattern
According to Head First: Design Pattern, the defition of strategy pattern (策略模式) is
family of algorithms, encapsulated each one, and makes them interchangeable. Strategy lets the algorithm vary independently from cloents that use it.
Strategy Pattern is a Behavioral Patterns.
Principle
- Take what varies or what might change and encapsulate(封装) it seperately.
- Program to an interface, not an inplementation
- Favor composition over inheritance, Has-a can be better than is-a.
Strategy Pattern encapsulates algotithm.
Pros & Cons
Pros
- Can easily change algorithm
- Avoid using many judge (
ifstatement) - Easily extantable
Cons
- Need many stategy classes
- All classes are expose to public
Strategy Pattern is suitable for when
- Many classes only have difference in behavior. This pattern allow object dynamically choose behacior within the interface.
- Dynamic algorithm
- A class have many behavior. Using other pattern need many
ifstatement.
Build
Context is a class using algorithm in stategy interface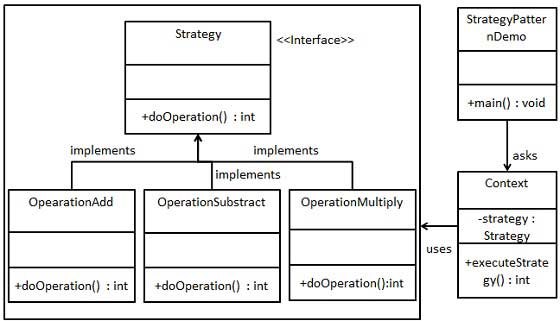
Interface
1 | public interface Strategy { |
Class in interfave
1 | public class OperationAdd implements Strategy{ |
1 | public class OperationSubtract implements Strategy{ |
1 | public class OperationMultiply implements Strategy{ |
Context
1 | public class Context { |
Implement
1 | public class StrategyPatternDemo { |
Result:
10 + 5 = 15
10 - 5 = 5
10 * 5 = 50
Strategy Pattern